Examples
Discover how Recapix transforms YouTube videos into clear and structured summaries.

DeepSeek is a Game Changer for AI
15mSummary
The video explains why the DeepSeek models (notably R1/V3) caused such a stir: they show that performance and training/inference costs can be improved without simply "scaling to infinity." The speaker puts this in the context of LLMs (Transformers, next-word prediction), the race for model size, and the "open" vs "closed" choices.
Key points:
- Reminder: an LLM is a large Transformer-based neural network that does next-word prediction.
- The "arms race" has mainly favored those with massive GPU resources and budgets.
- Difference between closed actors (API/product) and more open ones (publishing models).
- DeepSeek highlights efficiency gains and discusses mixture-of-experts approaches (activating part of the model instead of all of it).
- ... and 1 more points
Citations
"A large language model is a... Transformer based neural network that does next word prediction."
Takeaway:
Efficiency gains in AI models can come from architectural innovations like mixture-of-experts, not just scaling up.
YouTube · 15mWatch video →

How AI Image Generators Work (Stable Diffusion / DALL-E)
18mSummary
A pedagogical explanation of modern image generators: how a model goes from a "noisy" state to a coherent image, and how text guides the generation. The video mainly serves to clarify the principle (without requiring a huge math background).
Key points:
- Image generation = iterative process (progressive refinement).
- Text serves as a guiding signal to steer output toward requested content.
- Results strongly depend on the dataset and guidance: biases, styles, limitations.
- Difference in intuition: "creating" vs "reconstructing" from noise + constraints.
Takeaway:
AI image generation works through iterative denoising guided by text prompts, not by 'creating' images from scratch.
YouTube · 18mWatch video →

Public Key Cryptography
12mSummary
The video starts from "classic" (symmetric) encryption and shows its big practical problem: how to share the key securely. It then introduces asymmetric encryption with key pairs (public/private), and the idea of publishing your public key so anyone can encrypt a message intended for you.
Key points:
- Symmetric encryption: same key to encrypt/decrypt - key exchange problem.
- Asymmetric: two related keys (A/B) with distinct roles.
- The public key can be shared widely; the private one stays secret.
- Intuition: solving the paradox "I need a secure channel to share the key that gives me a secure channel."
Citations
"Your public key is public... you publish it everywhere..."
Takeaway:
Asymmetric encryption solves the key-sharing paradox by using a public/private key pair.
YouTube · 12mWatch video →
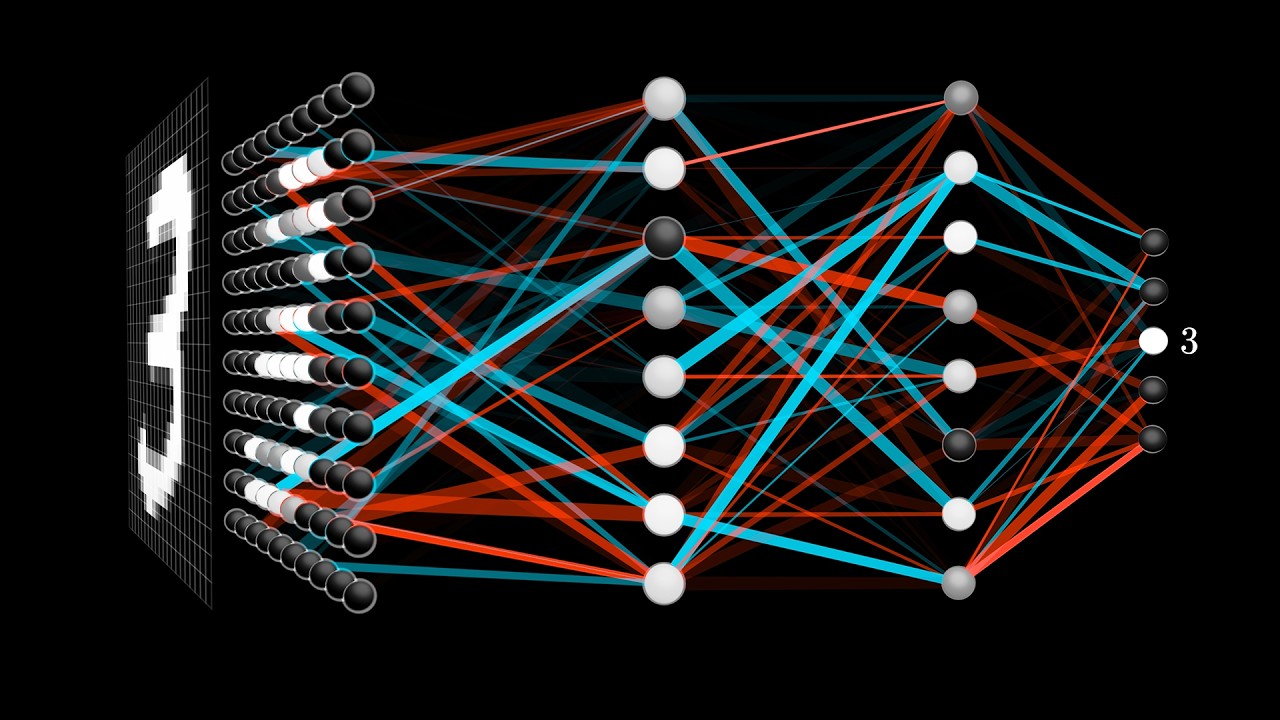
But what is a neural network? | Deep learning, chapter 1
19mSummary
A very visual introduction to neural networks, built around a concrete goal: recognizing handwritten digits. The video establishes the intuition of neurons, layers, and how a network represents a function that maps pixels to a prediction.
Key points:
- A network = layers of "neurons" that progressively transform input to output.
- Illustrative goal: classification of handwritten digits.
- "Understanding" comes from adjusted parameters (weights/biases), not hand-coded rules.
- Great revision support: you retain the intuition before tackling the math.
Takeaway:
Neural networks learn to recognize patterns by adjusting weights, not through hand-coded rules.
YouTube · 19mWatch video →

How to Start a Movement
3mSummary
Starting from an "absurd" dance sequence, Derek Sivers shows that the real start of a movement depends less on the "leader" than on the first follower who makes the action legitimate and imitable. Then, the movement grows by making participation simple and visible.
Key points:
- The "leader" isn't everything: the first follower transforms an isolated act into a movement.
- The leader's role: show how to follow, not just "be in front."
- The dynamic becomes collective as others join: it changes social perception.
Citations
"If you really care about starting a movement, have the courage to follow and show others how to follow."
Takeaway:
The first follower is as crucial as the leader in turning an isolated act into a movement.
YouTube · 3mWatch video →

How to Spot Fake News
8mSummary
The video offers simple reflexes to avoid spreading misinformation: verify via fact-checking sites, compare multiple reliable sources, and slow down before sharing (especially when content triggers an emotional reaction).
Key points:
- Use fact-checkers (examples cited: Snopes, PolitiFact).
- Cross-reference the info: source, date, context, wording.
- Beware of headlines designed to trigger emotion and push sharing.
Citations
"Look to fact checkers such as Snopes or PolitiFact..."
Takeaway:
Use fact-checkers and slow down before sharing—especially when content triggers strong emotions.
YouTube · 8mWatch video →

Explaining the Circular Economy and How Society Can Re-think Progress
4mSummary
An animation that contrasts "linear" economy (extract - make - dispose) with a "restorative" circular economy: rethinking product design so they can be repaired, reused, reconditioned, and powered by renewable energy.
Key points:
- Re-design: products "made to be made again," not thrown away.
- Less waste = less pressure on resources + new value chains.
- System vision: industry + energy + design + use.
Citations
"Made to be made again" (central idea repeated in the presentation).
Takeaway:
The circular economy aims to design products 'made to be made again', reducing waste and resource pressure.
YouTube · 4mWatch video →